Nicotine Stomatitis is a pathological change in mucosa of the Oral cavity caused due to cigar or pipe smoking which was very common in earlier days but has decreased in incidence with cigarette smoking. In Nicotine Stomatitis there is hyperkeratotic change in the oral mucosa caused due to heat produced from smoking and not due to chemicals produced from smoking. It results from chronic exposure of the palate to concentrated heat streams emanating from pipe or reverse smoking.
Long-term intake of extremely hot beverages has also been known to cause similar changes in the oral mucosa but most commonly it is associated with smoking and hence gets the name Nicotine Stomatitis. Totally reversible if the habit is stopped. Biopsy if you’re not sure of the diagnosis or if it looks suspicious. In South American and Southeast Asian regions it is called as “Reverse smoker’s palate” as people in these regions smoke hand-rolled cigarettes and cigars with the lit end inside the mouth.
Synonyms: Nicotine Palatinus, reverse smokers palate and Smoker’s Palate
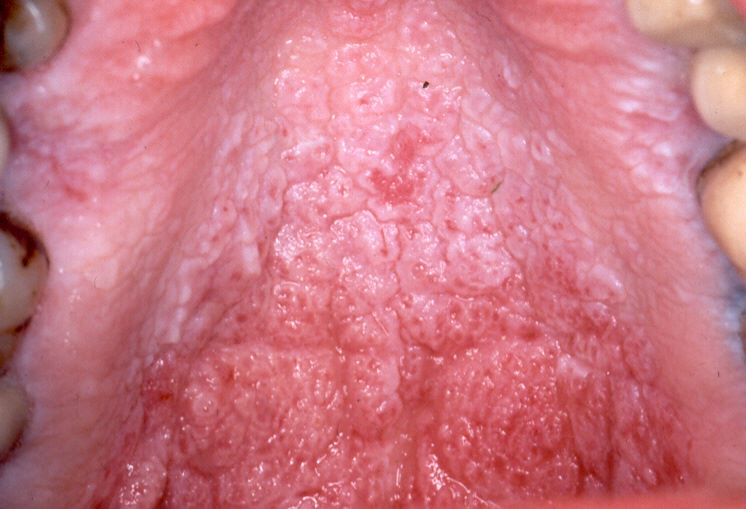
Clinical Features:
Nicotine stomatitis is seen in people older than 45 years as it is caused due to long term exposure to heat. Most commonly seen in Males who are common smokers. It appears a diffusely gray or white slightly elevated papules which are usually numerous in number and have punctate red centers as seen in the images. The teeth show characteristic brown or black stains as seen in tobacco smokers.
These structures are nothing but inflamed minor salivary glands and their ductal orifices. In some extreme cases the palate resembles ‘dried mud’ like appearance because of the fissures and thickened palatal keratin. Apart from the Palate the marginal gingiva and the interdental papillae are also involved along with the buccal mucosa which is occasionally seen.
Histological Features:
- The characteristic feature of Nicotine Stomatitis is the presence of hyperkeratosis and acanthosis of the palatal epithelium.
- Mild, patchy, chronic inflammation of subepithelial connective tissue and mucosal glands.
- Squamous metaplasia of the excretory ducts
- Inflammatory exudate is seen within the duct lumina
- Hyperplastic ductal epithelium is seen near orifice in cases with papular elevation
- Epithelial Dysplasia is rarely seen
Treatment and Prognosis:
Nicotine Stomatitis being a Benign condition is easily reversible with the cessation of habit. There are hardly any instances of malignant transformation seen. As this condition is caused due to exposure to heat over a prolonged duration of time, decreasing the area exposed to heat can help in curing the disease completely. Sources:”Image by Armando Lenis MD”
Sources: Image – Armando Lenis MD Sources: Pocket Atlas of Oral Diseases, Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology by Neville
Hi Varun,
I have found your information very helpful and I need to reference you in my university assignment.
Can I have the first letter of your first name please?
Yours faithfully
Bethan
Hi Bethan,
The first letter of my first name is – “P” Varun.