Denture-related stomatitis as the name suggests is Stomatitis or pain and inflammation of the mucous membrane of the mouth which is caused due to Denture in patients who wear a complete denture.
Denture Stomatitis Synonyms: denture sore mouth, Candida-associated denture-induced stomatitis, inflammatory papillary hyperplasia and denture-associated erythematous stomatitis.
Denture stomatitis is a common occurrence and it is a condition where there is some infection or redness of the oral mucous membrane beneath a denture. This occurs in people who are wearing dentures, and in about 90% of the cases, Candida species are involved. This is seen in 50% of the complete denture wearers.
Classification of Denture Stomatitis according to Newton:
Type 1:
Localized simple infection with pinpoint hyperemia. This is usually trauma induced.
Type 2:
Erythematous type. More diffuse erythema involving a part or the entire denture covered mucosa. This occurs due to microbial plaque accumulation.
Type 3:
Granular type involving the central part of the hard palate & alveolar ridge. Often seen in association with type I & type II. This too occurs due to microbial plaque accumulation.
Candida-associated denture stomatitis is often seen along with angular cheilitis (or) glossitis.
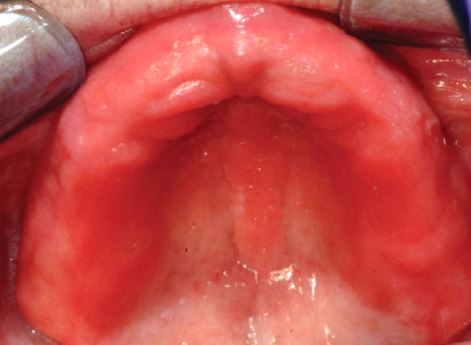
Image Credit: http://spectrum.diabetesjournals.org
Etiology – Causes of Denture Stomatitis
- Presence of the denture in the oral cavity both day and night
- Trauma from the denture in addition to plaque accumulation
These both are the direct factors for stomatitis related to dentures.
Who can get Denture stomatitis? Mainly the ones who cannot maintain a proper oral hygiene and keep their mouth clean. But it is also seen in diabetics as well as in people who take steroids either through inhalers or orally. Even a few antibiotics are known to cause this problem.
Predisposing Factors of Denture Stomatitis
These factors do not directly produce denture stomatitis but they favor the progress or initiation of the lesion.
Systemic Factors
- Old age
- Diabetes mellitus
- Nutritional deficiency
- Malignancy
- Immune defects
Local Factors
- Dentures: trauma, denture usage in the night, denture cleanliness
- Xerostomia: Sjogren’s syndrome, irradiation, drug therapy
- High carbohydrate diet
- Use of broad-spectrum antibiotics
- Smoking tobacco
Clinical Features of Denture Stomatitis
- Although symptoms are uncommon, the clinical presentation of erythema and edema in the part of the palatal mucous.
- At times, an obvious fungal infection in the form of white surface colonies or plaques may be observed on the mucosal surface.
- Variably intense erythema, which may also be associated with scattered petechiae, is distributed over the mucosa covered by the base of the denture but not beyond.
- Palpation of the involved mucosa reveals no tenderness or tissue friability.a covered by the denture base is a diagnostic finding.
- Intense erythema is the most common finding.
Diagnosis of Denture Stomatitis
The presence of candida associated denture stomatitis(CADS) is confirmed by the presence of mycelia or the pseudohyphae in a direct smear.
Supportive Measures
- Having efficient oral and denture hygiene habits.
- Correction of denture wearing habits.
- The patient is advised to store the dentures in 0.2 to 2% chlorhexidine during the night.
- The patient should be instructed to remove the denture after meals and scrub before reinserting it.
- The patient is advised not to use the dentures at night or leave it exposed to air.
Management of Denture Stomatitis
1. Drug Therapy
- Local therapy with nystatin.
- Amphotericin B & Clotrimazole for systemic therapy.
- Antifungal drugs: Given after the clinical diagnosis is confirmed,in patients with burning sensation of mucosa and where infection has spread to other sites of oral cavity & pharynx.
To reduce the risk of relapse: Continue the antifungal treatment for 4 weeks.
2. Surgical Management
- Includes the elimination of deep crypts in type III denture stomatitis.
- This is preferably done by cryosurgery.
i wear complete denture.
sore mouth and lips troubling me for a while
my gp advised swashing twice with hexidine
kinly advise for how many days i can safely use hxidine
Hello sir,
There isn’t any particular harm in using Chlorhexidine mouthwash or rinse, but we usually suggest to use for 15 days to 30 days depending on the condition which we are looking to treat. So you can use it for as many days as you feel that it might help.
If you want to use any mouthwash to numb the pain in the sore lips and mouth you can also try –
Mouthwash: “Coolora”
This helps in numbing the pain and can be used before you have a meal, it is not as an alternative to Hexidine mouthwash but just to help you eat well.
My doctor..diagnosed me with denture stomatitis she started me on fluconazole today. I’m in a lot of pain. Will this go away quickly
It does go away quickly make sure you do not use your Denture for the time being and give relief to the affected site.
dokk apakah bisa mengobati denture stomatitis dengan tantum verde??Trimakasi dok