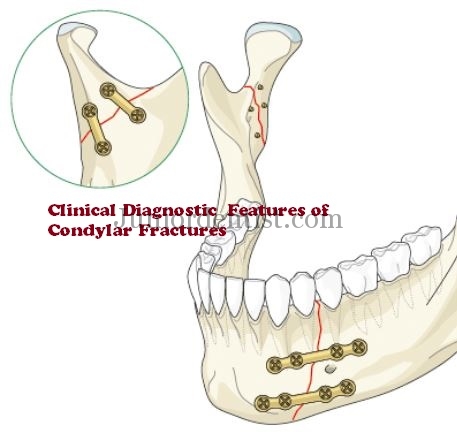
Condylar Fracture: Fracture of the Condylar Neck or Condylar Head either Unilateral or Bilateral depending on the location of impact or injury which is most commonly on the chin.
Radiographic examination is the most important diagnostic procedure to confirm Condylar fracture, but to diagnose condylar fracture clinical features are important to get to primary Diagnosis before you can get a Radiographic examination done.
Diagnostic Findings of Condylar Fractures:
- Evidence of facial trauma especially in the Mandibular and Symphysis region
- Localized pain and swelling in the region of TMJ
- Trismus or Limited Mouth Opening
- Deviation of Mandible towards the involved side
- Posterior Dental Open bite on the contralateral side
- Shift of dental occlusion towards the ipsilateral side with possible cross bite
- Blood in external auditory canal
- Lack of Condylar movement upon palpation
- Difficulty in lateral excrusion as well as protrusion
- The occurrence of anterior open bite with bilateral subcondylar fractures. this is associated with posterior gagging of the occlusion
- Persistent CSF leak through the ear is indicative of an associated fracture of the middle cranial fossa (Otorrhea)
Leave a Reply